In the rapidly evolving landscape of business, the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) presents both thrilling opportunities and daunting challenges. Many organizations find the allure of enhancing efficiency and driving innovation is tempered by a growing skepticism surrounding the limitations of AI. Is it truly a panacea for complex business problems? Or is it merely a tool with capabilities yet to be fully realized?
As decision-makers grapple with the implications of integrating AI into their business models, they face a myriad of perspectives on its efficacy. Some celebrate advances like AlphaFold and Grok4, heralding them as revolutionary breakthroughs that could redefine industries. Meanwhile, others caution that AI cannot wholly replace human ingenuity or creativity, nor can it resolve the multifaceted issues businesses encounter.
These discussions expose a fundamental question: What truly constitutes the limitations of AI? How can businesses navigate this new terrain while remaining vigilant to its potential shortfalls? This article seeks to explore these critical facets of AI adoption and the diverse viewpoints surrounding its integration into business strategies.


Adopting Artificial Intelligence in Business
Adopting artificial intelligence (AI) can significantly transform business operations, yet many companies encounter barriers that prevent seamless integration. Understanding these common challenges can help organizations strategize effectively for AI adoption. Here are some prevalent obstacles that hinder progress:
- Lack of Expertise: There is often a shortage of skilled professionals who can develop and implement AI systems. Companies may struggle to recruit personnel who possess the necessary technical knowledge and experience with AI technologies.
- Privacy Concerns: AI systems frequently require vast amounts of data for training and decision-making processes. This can raise significant privacy issues, leading to fears about data misuse and compliance with regulations, such as GDPR. Organizations may be hesitant to move forward due to potential legal repercussions.
- Security Risks: The deployment of AI introduces new vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious actors. Companies must grapple with the potential for data breaches and the consequences of insecure AI applications, leading to reluctance in adoption.
- Cost of Implementation: The financial investment required to integrate AI technologies can be a significant barrier. High costs associated with acquiring technology, hiring talent, and ongoing maintenance can deter organizations from pursuing AI initiatives.
- Cultural Resistance: Organizational culture can influence the adoption of AI. Employees may resist changes brought by AI technologies, fearing job loss or disruption to established processes. Overcoming this reluctance is essential for successful integration.
- Lack of Clear Strategy: Without a well-defined strategy for AI implementation, organizations may struggle to realize its benefits. A failure to align AI projects with business goals can lead to wasted resources and incomplete initiatives.
By acknowledging and addressing these barriers, companies can pave a clearer path for effective AI adoption, ensuring they capitalize on its potential while managing associated risks.
| AI Tool | Features | Use Cases | Adoption Barriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | Natural language processing, conversational capabilities | Customer support, content generation | Requires fine-tuning, potential bias |
| AlphaFold | Protein structure prediction | Drug discovery, biomedical research | Complexity in implementation, high computational resources |
| Grok4 | Automated software development | Rapid prototyping, code generation | High cost, requires specialized knowledge |
| Stable Diffusion Models | Advanced imaging techniques, enhanced diagnostic capabilities | Medical imaging, tumor detection | Data privacy concerns, need for extensive datasets |
In the realm of creative tasks, there has long been a steadfast belief that human ingenuity could not be easily replicated by artificial intelligence (AI). This sentiment was prevalent just a few years back, encapsulated in the assertion, “The argument that creative tasks cannot easily be substituted by AI was a common belief just five years ago.” Notably, the narrative surrounding AI and creativity has shifted significantly, reflecting broader societal changes and advancements in technology.
Historically, the creative domain—encompassing areas such as art, music, and writing—was perceived as a uniquely human endeavor. The creative process was thought to be inherently complex, rooted in emotions, experiences, and a nuanced understanding of the world. Critics posited that AI could assist in creative ventures but could never truly replicate the intrinsic human qualities that drive authentic creativity.
As AI technology has advanced, these assumptions have come under scrutiny. For instance, in recent years, AI systems capable of generating art, music, and even written content have surfaced. Platforms like DALL-E and OpenAI’s ChatGPT have demonstrated capabilities that some argue rival human creativity by producing artworks and composing text in response to user prompts. This development has not only challenged traditional views but has spurred debates about the essence of creativity itself.
A prime example of this paradigm shift can be seen in the marketing sector. Five years ago, many industry leaders doubted the effectiveness of AI in crafting compelling narratives or designing visually striking advertisements. Today, however, AI-generated campaigns are increasingly commonplace, with brands leveraging these tools to enhance their creative processes. Companies are recognizing that AI can augment human creativity, offering new perspectives, generating ideas, and even streamlining workflows.
Moreover, the utilization of AI in creative processes can lead to unprecedented levels of innovation. By combining human intuition with AI’s analytical capabilities, teams can explore creative avenues that were previously unthinkable. This fusion of human and machine creativity is beginning to redefine what creative tasks entail.
In summary, the belief that creative tasks are reserved solely for humans is evolving. Today, many accept that while AI may not fully replace human creativity, it can complement and enhance it in ways that were once considered impossible. The tide is shifting, reflecting not only technological advancement but also a broader rethinking of creativity in an AI-infused world.
Significant AI Success Stories
Artificial intelligence (AI) has significantly transformed various business models by overcoming traditional limitations and instilling confidence in AI tools. Notable examples include DeepMind’s AlphaFold in protein structure prediction and the emergence of AI-driven platforms in software development.
AlphaFold: Revolutionizing Protein Structure Prediction
AlphaFold, developed by DeepMind, has made groundbreaking advancements in predicting the three-dimensional structures of proteins from their amino acid sequences. This achievement addresses a longstanding challenge in biology and has profound implications for drug discovery and disease understanding.
- Nobel Prize Recognition: In 2024, Demis Hassabis and John Jumper of DeepMind were awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for developing AlphaFold. Their work has significantly accelerated biochemical research by providing accurate protein structures, which are crucial for understanding biological processes and developing new therapies. Source
- Accelerated Drug Discovery: AlphaFold’s predictions have been instrumental in identifying potential drug targets. For instance, researchers utilized AlphaFold to predict the structure of Cyclin-dependent Kinase 20 (CDK20), leading to the discovery of a novel small molecule inhibitor within 30 days—a process that traditionally takes much longer. Source
- Global Impact: The AlphaFold Protein Structure Database has been accessed by over 2 million researchers across more than 190 countries, saving an estimated 1 billion research years. This widespread adoption underscores the tool’s reliability and the confidence the scientific community places in AI-driven solutions. Source
AI in Software Development: Enhancing Efficiency and Innovation
While specific details about “Grok4” are not available, AI has broadly impacted software development by automating tasks, improving code quality, and fostering innovation.
- Automated Code Generation: AI-powered tools can generate code snippets, reducing development time and minimizing human error.
- Bug Detection and Resolution: Machine learning algorithms analyze code to identify potential bugs and suggest fixes, enhancing software reliability.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) Integration: AI models interpret and generate human-like text, enabling more intuitive user interfaces and improving user experience.
These advancements demonstrate AI’s capability to overcome traditional limitations in software development, leading to more efficient processes and higher-quality products.
In summary, AI’s integration into fields like protein structure prediction and software development showcases its potential to address complex challenges, streamline processes, and instill confidence in AI-driven tools across various industries.
In conclusion, the journey towards AI adoption reflects a complex interplay of excitement and skepticism, highlighting the nuanced relationship between artificial intelligence and business models. As discussed throughout this article, AI offers remarkable tools that can drive innovation, exemplified by breakthroughs like AlphaFold and Grok4. However, each advancement comes with critical limitations that necessitate a thoughtful approach to integration.
Understanding the constraints—be it the need for extensive data, concerns about privacy, or the inherent risks of AI technology—is essential for organizations aiming to leverage these tools effectively. As echoed in the conversation surrounding creative tasks, the narrative is evolving: while AI cannot fully replicate the human touch, it certainly holds the potential to augment our capabilities, leading to fresh perspectives and innovative solutions.
Reflecting on this dynamic, we recognize that businesses must strike a balance—embracing AI’s potential while remaining acutely aware of its limitations. As Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, insightfully stated, “AI cannot replace human qualities like creativity, empathy, and judgment. Instead, AI will amplify our human capabilities and help cultivate our creative spirit.” The future landscape will require leaders who are not only technologically savvy but also capable of fostering a collaborative environment that blends human ingenuity with machine efficiency.
As we look ahead, the question remains: how will organizations adapt to this shifting paradigm? Companies must not only commit to investing in AI but also in the continuous learning necessary to navigate its evolving complexities. Ultimately, those that succeed will be the ones that understand AI as an ally rather than a competitor, utilizing it to elevate their business strategies in an increasingly digital world.
AI User Adoption Rates Across Industries
Artificial intelligence (AI) adoption reveals a stark contrast across various industries, marked by significant discrepancies in integration rates. According to recent statistics:
- Information and Communication: This sector leads in AI adoption, with approximately 48.72% of firms in the EU utilizing AI technologies. This strong inclination showcases how digital transformation is deeply rooted in enhancing efficiencies and customer interactions. [DesignRush]
- Professional and Scientific Services: Following closely, about 30.53% of companies in this industry have adopted AI, indicating a positive trend towards leveraging technology for innovation. [DesignRush]
- Healthcare: Contrasting the previous sectors, only 15% of healthcare organizations report using AI. This highlights the industry’s hesitance, as decision-makers grapple with regulatory compliance, ethical considerations, and the high stakes involved in patient care. [Banshee]
- Construction: Alarmingly, this industry has the lowest adoption rate at a mere 1.4%. Factors such as reliance on traditional practices, fear of disrupting ongoing projects, and risk aversion contribute to this stagnation. [Bipartisan Policy Center]
Barriers to AI Adoption
Numerous challenges hinder AI integration, including:
- High Initial Costs: The substantial investment needed for AI implementation can deter organizations, especially small and medium-sized enterprises. This financial burden makes it difficult for many to take the leap into AI. [Supply Chain Brain]
- Data Quality and Fragmentation: Successful AI initiatives require cohesive and high-quality data. About 47% of manufacturing firms note that fragmented data poses a serious impediment to AI adoption. [Supply Chain Brain]
- Skill Gaps: The scarcity of professionals skilled in AI technologies is significant, with 54% of workers in manufacturing needing substantial training to adapt to new AI-driven roles by 2025. [Supply Chain Brain]
- Resistance to Change: Employee fears of job displacement due to AI technology often result in skepticism and reluctance towards adoption. Amongst change-averse cultures, this resistance can severely impact AI integration efforts. [Supply Chain Brain]
Noteworthy Trends and Observations
The variance in AI adoption rates prompts further scrutiny into sector-specific disparities:
- Manufacturing: While growth in AI adoption is noted, accuracy concerns, particularly over AI’s “hallucinations,” lead many manufacturers to adopt a cautious approach. [Reuters]
- Healthcare: Regulatory hurdles and the imperative for safety in this high-stakes field create a slower adoption timeline relative to other sectors. [Banshee]
- Construction: The industry’s traditional reliance on manual tasks and a focus on precision hinder progressive adoption of AI solutions. [TechTarget]
In summary, AI adoption rates reveal both enthusiasm and skepticism across sectors, framing a complex landscape of opportunities and challenges. Organizations that understand and address these barriers will be better positioned to integrate AI effectively into their business models, unlocking its full potential.
Insights from Industry Experts on AI Limitations and Future Potential
In discussions surrounding artificial intelligence (AI), experts frequently highlight both the limitations and the transformative potential of this technology. Below are notable insights that add depth to our understanding of AI’s role in business and society:
-
Sam Altman, CEO of OpenAI, has expressed concern regarding society’s growing reliance on AI systems like ChatGPT. He remarked, “It’s worrying and potentially dangerous that many young users are deferring major life decisions to AI,” underscoring the ethical dilemmas that arise as AI takes on more decision-making responsibilities.
Source -
Ray Kurzweil, a renowned futurist, has predicted that we could see the emergence of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) by 2029, stating AI’s capability to redefine fields such as drug discovery through advanced simulations. This quote reflects both optimism about technological advancements and caution about the challenges that AGI may present.
Source -
Jensen Huang, CEO of Nvidia, acknowledges the concerns about job displacement due to AI, but he emphasizes that this outcome is contingent upon society’s ability to continue innovating. He points out that, “Such losses are likely only if we fail to keep advancing.”
Source -
Bill Gates, co-founder of Microsoft, has highlighted the need for responsible AI development. He warns that as AI grows more powerful, it is essential to align it with human values and interests to prevent misalignment.
Source -
Sundar Pichai, CEO of Google, believes that AI’s transformative potential has the capability to surpass foundational technologies, revolutionizing industries such as education, healthcare, and beyond. This vision emphasizes the widespread implications of AI.
Source -
Tim Cook, CEO of Apple, has reiterated that the future of AI depends significantly on ethical considerations in its development. He advocates for a balanced approach that prioritizes responsible uses of technology.
Source -
Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, promotes the integration of ethical considerations into AI development and stresses addressing complex global challenges such as climate change through AI solutions that serve humanity’s best interests.
Source -
Sheryl Sandberg, former COO of Facebook, acknowledges AI’s potential to tackle global challenges but emphasizes that its true power will emerge when human creativity collaborates effectively with AI’s analytical capabilities.
Source -
Suzie Compton, Senior Director at Salesforce, points out the vital responsibility that accompanies AI’s influence, emphasizing the need to balance speed and innovation with safety considerations in areas such as security and privacy.
Source -
Timnit Gebru, Founder of the Distributed AI Research Institute, emphasizes the urgent need for a regulatory framework for AI algorithms, advocating for checks and balances that ensure bias testing and accountability in AI applications.
Source
These expert insights illustrate the dual nature of AI as a tool for innovation while also highlighting the critical ethical considerations that accompany its advancement. As organizations navigate the complexities of AI adoption, these perspectives serve as essential guideposts for responsible implementation.
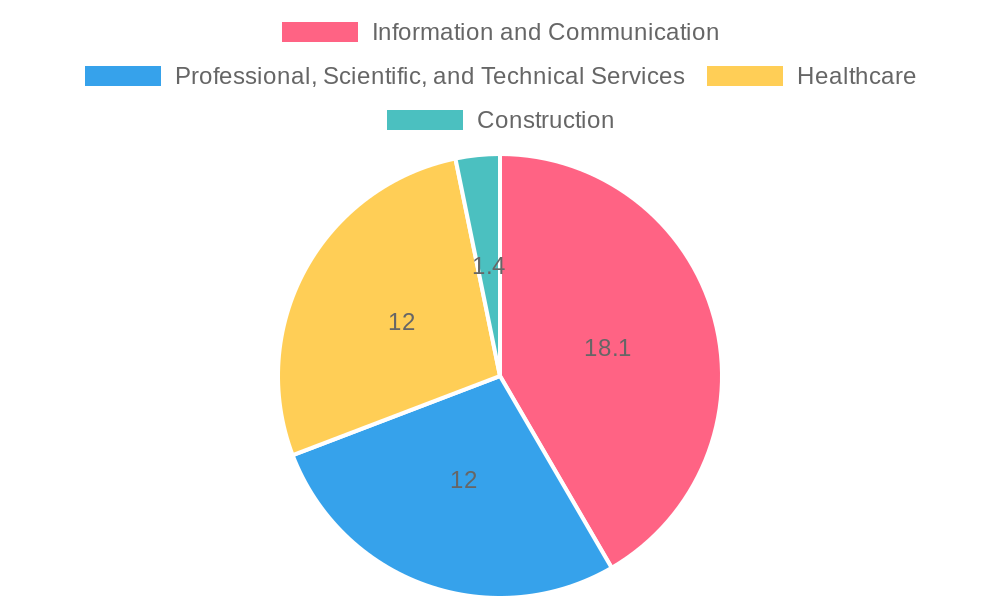
This pie chart illustrates the varying levels of AI adoption across industries: 18.1% in Information and Communication, 12% in Professional, Scientific, and Technical Services, 12% in Healthcare, and a mere 1.4% in Construction, highlighting significant discrepancies in how different sectors are embracing AI technology.
Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Automation into Business Models
Integrating artificial intelligence (AI) and automation into business models offers transformative potential but also presents significant challenges. Key issues include AI integration challenges, data privacy concerns, and aligning AI with business strategy.
AI Integration Challenges
Many organizations struggle to move beyond pilot phases due to fragmented data and poor integration with existing systems. Effective AI implementation requires structured, accessible data integrated into core workflows. Simply automating basic tasks is insufficient; businesses must adopt advanced systems that augment human decision-making. A major obstacle is the complexity of integrating AI with legacy infrastructure and multiple data systems, which can prevent AI tools from delivering meaningful insights. Process mapping, data organization, and choosing platform-based, low-code AI tools are essential for easier deployment and scalability. Source
Additionally, AI agents are not immune to the long-standing issue of silos in enterprise IT. Many organizations use agents in isolated roles without integration, limiting collaboration and undermining productivity. To maximize agent potential, businesses should create a unified data fabric, deploy a hybrid control plane, and build a central hub for agent orchestration. Source
Data Privacy in AI
The rapid adoption of AI has resurfaced the longstanding issue of data sprawl, now with greater urgency. AI not only consumes but also generates vast new quantities of data, including reports, logs, and metadata. Without structured governance, this data overload becomes a significant security risk, with attackers targeting poorly managed or forgotten data repositories. Traditional manual approaches are infeasible for managing this challenge, and proactive strategies are essential to prevent severe cyber risks. Source
Furthermore, data privacy has evolved from being solely a legal and compliance issue to a core accountability for IT departments. Organizations face heightened scrutiny from boards, regulators, and auditors, and IT leaders are now expected to oversee data privacy compliance, manage third-party risks, and address AI governance—often without sufficient resources or organizational authority. To address these issues, best practices such as dynamic data mapping for visibility, automation to streamline compliance tasks, and AI agents to manage risk and automate core privacy functions are recommended. Source
AI in Business Strategy
Despite 93% of organizations using AI, only 7% have fully embedded governance frameworks, and just 8% have integrated AI governance into their software development lifecycles. Many businesses continue to follow outdated software practices that fail to address AI-specific risks such as bias, lack of explainability, and hallucinations. Key challenges include inadequate infrastructure, poor tooling, limited bias and interpretability testing, and fragmented governance efforts. Just 4% of organizations feel prepared to support AI at scale, and most lack essential features like audit trails and version control. AI oversight is often siloed at departmental levels rather than being strategically led, with only 18% using KPIs for continuous monitoring. Cross-functional collaboration remains limited, with few involving ethics, legal, or HR teams in AI decision-making. Unchecked AI deployment can lead to significant risks, including privacy breaches and loss of trust. Organizations are urged to align AI strategies with business goals, invest in infrastructure, and establish clear, cross-functional accountability to ensure resilient and ethical AI implementation. Source
In conclusion, while AI and automation offer substantial benefits, addressing integration challenges, ensuring data privacy, and aligning AI initiatives with business strategy are crucial for successful adoption.

