Agentic Orchestration
Agentic orchestration coordinates autonomous AI agents to execute complex workflows reliably and at scale. By design, it merges orchestration, governance, and decision-making into a single execution layer. It is transforming how enterprises build automation and mixed workforce systems.
As organizations adopt agentic AI, integration gaps cause most projects to stall. However, the problem rarely lies with the models themselves. Instead, fragile processes, poor data quality, and missing governance break execution. Therefore, agentic orchestration matters because it enforces controls and measures outcomes.
Orchestration ensures each AI agent acts within policy and logs every decision. Moreover, it ties outputs to business KPIs and audit trails. As a result, teams can trust AI-driven automation and scale with confidence. This article explains the non-AI foundations enterprises must build to turn experimentation into measurable results.
Start with clean data and clear process maps before layering agents. Because AI agents depend on trusted inputs, data quality becomes a competitive advantage. Moreover, governance and role-based access control prevent costly errors and compliance failures. Change management prepares people to work with agents, not replace them. Ultimately, agentic orchestration converts prototypes into measurable business value and resilience. Read on to learn the practical non-AI steps that deliver real ROI.
Agentic Orchestration Fundamentals
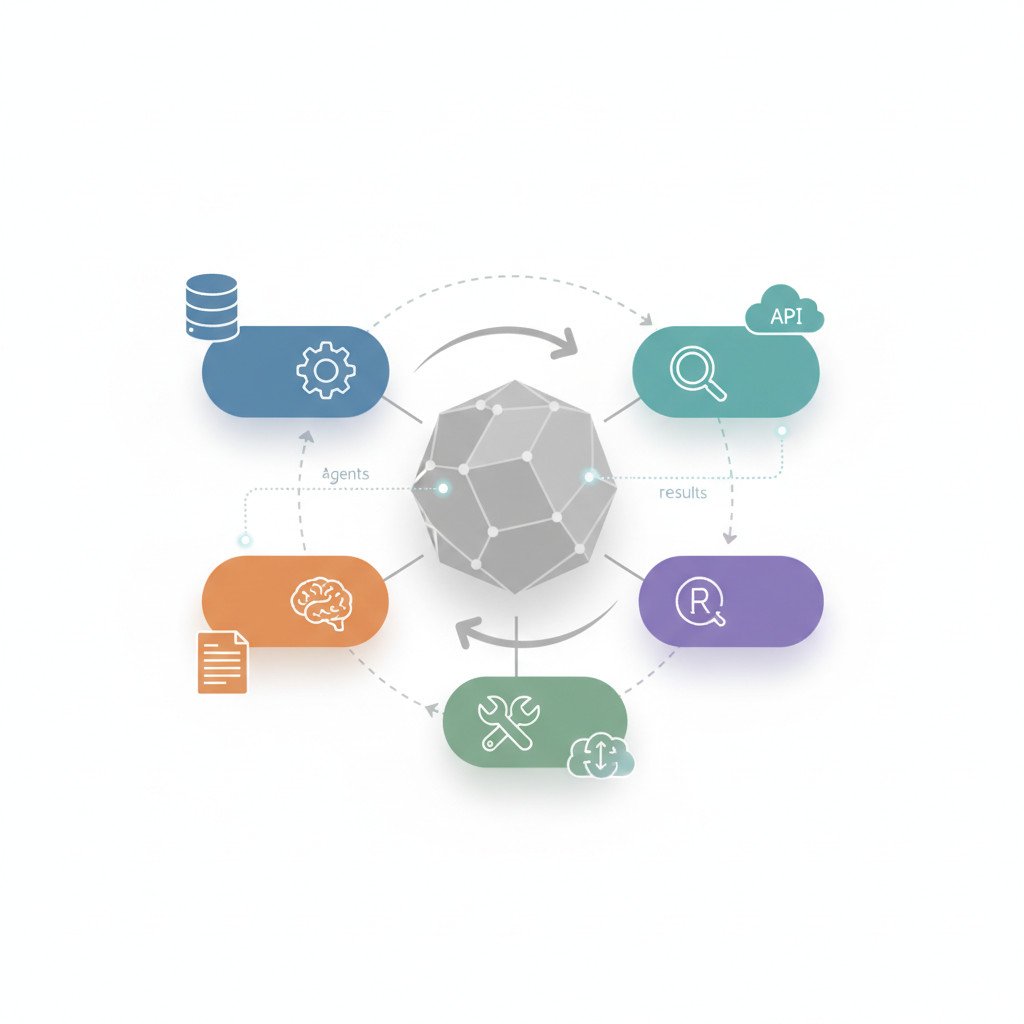
Agentic orchestration coordinates multiple autonomous AI agents so they act as a single, reliable workflow engine. It links decision making, execution, and governance in one control layer. Because it centralizes control, teams can scale complex automation with confidence.
Core concepts in plain language
- AI agents are focused programs that perform tasks such as reading documents or calling services.
- The control plane routes tasks to the right agent, and it enforces policy and access rules.
- A data layer supplies clean, governed inputs and receives validated outputs.
- Observability logs decisions and metrics for audit and measurement.
- Governance enforces compliance checks, role based access, and approval gates.
How agentic orchestration works in theory
- A trigger fires, for example a customer request or a process event.
- The orchestrator picks the best agent or combination of agents for the job.
- Agents run, share intermediate results, and call services as needed.
- The orchestrator validates outputs against business rules and quality checks.
- Finally, the system records actions to audit logs and maps results to KPIs.
This flow keeps execution reliable and measurable. Moreover, it isolates faults so teams can retry or roll back specific agents. Therefore, orchestration reduces risk while improving speed.
Why this matters today
Enterprises face brittle integrations that stop pilots from scaling, according to recent reporting on an MIT study that found many generative AI projects deliver no measurable impact [Toms Hardware]. As a result, agentic orchestration becomes the enabler that ties agents to real business outcomes.
For example, factories use agentic orchestration to keep production evergreen and resilient, which you can read about in this article [How Do Industry 4 0 and agentic orchestration Deliver Evergreen Transformation for Factories?]. In addition, data quality and governance remain the foundations of success, so review this guide for deeper context [Why Are Data Quality and Governance the Real Foundations for Agentic AI Success?]. Finally, modern toolchains and gateways change how agents connect to services, as explored in this piece [Why IBMs MCP Gateway Will Revolutionize AI Toolchains Forever].
In short, agentic orchestration turns fragile agent experiments into dependable, governed automation that maps to business value. Consequently, it is a must have capability for AI driven enterprises.
Benefits of Agentic Orchestration
Agentic orchestration delivers clear business and technical benefits. It reduces manual coordination, speeds execution, and unlocks new kinds of automation. Below are the major payoffs teams report.
- Efficiency and cost reduction
- Orchestrators route tasks to the most suitable agent, removing idle time and duplication. As a result, throughput increases while costs drop.
- Example: a finance process that once needed five handoffs now runs with three agents and one human reviewer. Cycle time fell by 60 percent.
- Scalable automation
- Because orchestration centralizes control, businesses scale agents horizontally and vertically. Moreover, the same control plane manages hundreds of concurrent workflows.
- Example: a customer support pipeline handled seasonal spikes without adding staff by spinning more agents.
- Higher reliability and reduced risk
- Orchestration enforces validation, retries, and rollback rules. Consequently, failures stay contained and easy to fix.
- Example: RBAC and automated logging prevented a compliance lapse in a healthcare pilot, and auditors accepted the evidence.
- Faster innovation
- Teams can assemble new workflows by composing existing agents. Therefore, experiments move from concept to production faster.
- Example: combining an IDP agent with a fulfillment agent created a new order-to-fulfill flow in weeks.
- Measurable outcomes and governance
- Orchestration maps agent actions to KPIs, audit logs, and compliance checkpoints. As a result, leaders can measure ROI and explain decisions.
- Moreover, observability enables continuous improvement.
- Better data and model hygiene
- The orchestrator enforces data contracts and quality checks. Therefore, agents consume trusted inputs and produce reliable outputs.
- Investment in data quality yields higher adoption and fewer errors.
- Human-machine collaboration
- Agentic orchestration supports approval gates and escalation rules. Thus, agents augment knowledge workers rather than replace them.
- Training and change management make this shift smoother.
In short, agentic orchestration raises speed, scale, trust, and innovation. Consequently, organizations convert agentic AI experiments into measurable business value. Start today.
Traditional Automation versus Agentic Orchestration
| Features | Traditional Automation | Agentic Orchestration | Benefits of Agentic Orchestration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decision making | Rules driven and deterministic. | Distributed among autonomous agents with a control plane. | Enables dynamic task allocation and adaptive decisions. |
| Scalability | Scales by adding scripts or robots. | Scales horizontally by adding agent instances and pipelines. | Handles spikes with less manual effort. |
| Fault tolerance | Failures often stop the whole process. | Isolates faults to specific agents and retries. | Reduces blast radius and speeds recovery. |
| Data handling | Tightly coupled to rigid inputs. | Enforces data contracts and quality checks. | Produces more reliable outputs and fewer errors. |
| Governance and compliance | Manual logging and audits. | Automated RBAC, audit trails, and checkpoints. | Improves traceability and regulatory readiness. |
| Human in the loop | Humans perform approvals and fixes. | Supports approval gates and escalations. | Augments workers and preserves institutional knowledge. |
| Speed of innovation | New flows require heavy engineering. | Compose agents to build flows quickly. | Shortens time from experiment to production. |
| Observability | Limited metrics and opaque failures. | Centralized logging and KPI mapping. | Enables measurable ROI and continuous improvement. |
| Integration complexity | Point to point integrations proliferate. | Uses gateways and standardized interfaces. | Simplifies toolchain management and upgrades. |
| Reusability | Hard to reuse components across processes. | Agents are modular and composable. | Lowers development cost and accelerates reuse. |
Real-World Use Cases
Agentic orchestration unlocks practical value across industries. Because agents can coordinate autonomously, teams solve problems that once required heavy manual work.
Marketing and personalization
-
Use case: Orchestrators combine content generation agents, personalization agents, and delivery agents. As a result, campaigns adapt in real time to customer signals.
-
Example: A retail brand runs personalized promotions during a sale. Agents select offers, generate creatives, and route ads to the best channels. Consequently, conversion rises while manual setup drops.
Sales automation and lead triage
-
Use case: Sales teams use orchestrated agents to score leads, enrich profiles, and schedule outreach.
-
Example: An agent pipeline filters high intent leads, drafts tailored messages, and books discovery calls. Therefore, reps focus on closing, not admin.
Customer service and support
-
Use case: Orchestration chains conversational AI, knowledge retrieval, and backend systems. This makes answers accurate and actions immediate.
-
Example: When a customer reports an issue, agents fetch order data, propose fixes, and escalate when needed. Moreover, the system logs every step for audits.
Manufacturing and Industry 4.0
-
Use case: Factories coordinate condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, and scheduling agents. As a result, downtime falls and throughput rises.
-
Example: Sensors trigger agents that diagnose anomalies, order parts, and reschedule shifts. In practice, this keeps assembly lines resilient.
Finance, compliance, and procurement
-
Use case: Agentic pipelines validate invoices, check policy, and route approvals. Therefore, teams achieve faster processing and stronger controls.
-
Example: An orchestrator enforces data contracts and RBAC. Consequently, auditors find clear trails and compliance improves.
IT operations and DevOps
-
Use case: Orchestrated agents detect incidents, run triage playbooks, and roll back changes when necessary.
-
Example: During a service outage, agents isolate causes, notify owners, and trigger remediation bots. Thus, mean time to repair falls.
In short, agentic orchestration turns discrete AI capabilities into end-to-end solutions. Because it emphasizes governance and observability, enterprises gain speed, trust, and measurable outcomes.

Challenges and Considerations
Agentic orchestration unlocks value, but it is not risk free. Leaders must weigh technical, legal, and operational trade offs before wide adoption.
- Technical complexity and integration
- Orchestrators must connect to legacy systems and modern APIs. Because of this, integration plans need clear interfaces and fallbacks.
- Teams should design retry logic, circuit breakers, and visible error states. Otherwise, small failures can cascade across agents.
- Moreover, observability must track data lineage and decision provenance for debugging and audits.
- Data privacy and security
- Agents often access sensitive records and customer data. Therefore, apply strict encryption, tokenization, and least privilege controls.
- Role based access control and automated logging reduce insider risk and support audits. As a result, compliance becomes easier to demonstrate.
- Governance and model risk
- Models can drift and produce biased outputs over time. Consequently, set guardrails for validation, human review, and model refresh.
- Establish approval gates and ethical checkpoints so decisions remain explainable and defensible.
- Operational and cultural change
- Teams must shift from task execution to oversight and exception handling. Training helps staff trust and work with agents.
- In addition, clear process maps and ownership prevent duplicated responsibilities.
- Cost and vendor lock in
- Running many agents increases compute and data costs. Therefore, measure total cost of ownership and start with high impact pilots.
- Also, design for portability to avoid tight coupling with a single vendor or proprietary gateway.
In short, agentic orchestration requires careful preparation. When firms address these concerns, they gain scalable automation that remains secure and auditable.
Future Trends in Agentic Orchestration
Agentic orchestration will evolve quickly as tooling and expectations mature. Designers will build smarter control planes that coordinate hundreds of AI agents. As a result, workflows will adapt in real time to changing business signals.
Key innovations to watch
- Federated and decentralized orchestration
- Orchestrators will support federated agents across cloud and edge. Therefore, teams can keep sensitive data local while agents collaborate.
- Native policy and compliance engines
- Orchestration layers will include built in governance for RBAC and audits. Moreover, automated ethical checks will reduce model risk.
- Explainability and provenance by design
- Future platforms will capture decision lineage automatically. Consequently, leaders can trace outcomes to agent actions and inputs.
- Auto orchestration and meta learning
- Systems will learn which agent compositions work best. As a result, the orchestrator will recommend or auto create pipelines.
- Plug and play agent marketplaces
- Vendors and internal teams will publish reusable agents and connectors. Therefore, composability will accelerate innovation.
- Cost aware orchestration
- Orchestrators will balance performance and cost across models. Thus, organizations will manage total cost of ownership more tightly.
A mixed workforce will become the norm. People will focus on exceptions and strategy, while agents handle routine work. In short, agentic orchestration will move from experiments to mission critical systems. Consequently, firms that invest in data quality, governance, and process readiness will lead the next wave of innovation.
Agentic orchestration ties autonomous agents to reliable, governed outcomes. It depends on clean data, clear processes, and strong governance. Therefore, firms that prepare these non AI foundations turn pilots into measurable business value.
EMP0 stands out as a practical partner for this journey. For example, EMP0 designs end to end agentic orchestration solutions that include data quality, governance, and change management. Moreover, EMP0 provides tools that let teams build, test, and deploy agent pipelines safely and quickly.
What EMP0 offers
- Strategy and consulting to align agents with business KPIs
- Agentic Orchestration platforms and connectors for enterprise systems
- Data quality, governance, and RBAC frameworks to secure workflows
- Training, workshops, and change programs to enable a mixed workforce
- Reusable agents and accelerators such as Agent Builder and IDP for faster delivery
Start small, scale responsibly, and measure what matters. Because agentic orchestration can fail without the right foundations, EMP0 helps you prioritize data, governance, and process design first. As a result, teams gain trust and reduce risk while accelerating innovation.
Explore EMP0 to learn how agentic orchestration can power AI driven growth systems for your business. Visit the EMP0 profiles below for tools, articles, and creator resources.
Download The Definitive Guide to Agentic Orchestration and begin preparing your enterprise for durable, auditable, and high impact AI automation.

