Bloom Open-Source Agentic Framework
Bloom open-source agentic framework for automated behavioral evaluations of frontier AI models delivers scalable, measurable behavioral tests for frontier AI. It automates seed driven generation, judgment, and meta-judgment across simulated rollouts. This agentic system uses seed.yaml and behaviors.json to define target behaviors.
Because automated behavioral evaluations scale better than manual tests, they reduce oversight gaps. Moreover, Bloom integrates LiteLLM, Anthropic, and OpenAI backends through one unified interface. Therefore teams can run large sweeps with Weights and Biases and Inspect exports.
Anthropic used Bloom to build alignment relevant suites with hundreds of behavior consistent rollouts. As a result, evaluators gain quantitative metrics like elicitation rate and reproducible transcripts. In short, Bloom accelerates frontier AI safety research while providing open-source transparency and extensibility.
It ships as a Python pipeline under the MIT license on GitHub for immediate adoption. Therefore researchers and engineers can iterate faster, test edge behaviors, and quantify risks. Join the community to extend and validate evaluations.
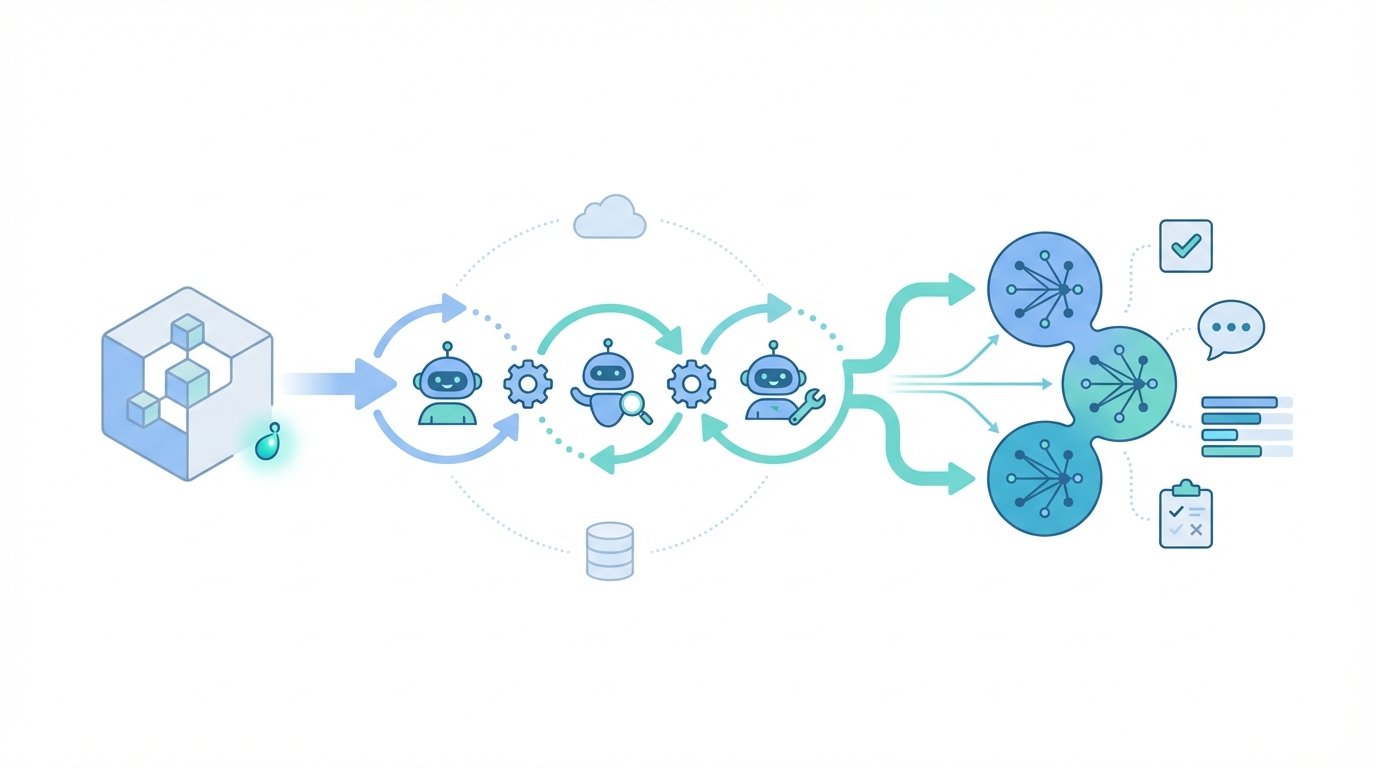
Bloom is an open source agentic framework that automates behavioral evaluations for frontier AI. It runs a Python pipeline that turns a single behavior definition into many rollouts. Because it uses agents to ideate and judge scenarios, Bloom produces behavior consistent transcripts at scale.
At the core sits a seed configuration. The seed files seed.yaml and behaviors.json define target behaviors, role prompts, and run parameters. For example, seed.yaml encodes the initial scenario and constraints. Therefore Bloom expands that seed into diverse simulated rollouts automatically.
This automation matters for frontier AI safety and performance. It scales testing far beyond manual labeling, and it finds edge behaviors faster. Moreover, Bloom integrates with model backends and tooling, including Anthropic models at Anthropic and Weights and Biases at Weights and Biases. As a result teams can run large sweeps and export Inspect compatible transcripts.
Bloom ships under an MIT license and encourages community extensions. Researchers can fork the pipeline, add judge models, and measure elicitation rates. In short, Bloom accelerates reproducible, quantitative behavioral evaluations for cutting edge models.
Below is a concise comparison that highlights Bloom’s strengths for behavior-driven evaluation.
Moreover, it focuses on automation, reproducibility, and scalable sweeps.
| Feature | Bloom | Petri | Traditional testing |
|---|---|---|---|
| License type | MIT open source, GitHub-ready | Research or prototype; varies | Proprietary or ad hoc |
| Evaluation methodology | Agentic pipeline: Understanding, Ideation, Rollout, Judgment | Scripted benchmarks and curated tests | Manual scenario design with human labeling |
| Model integration | LiteLLM backend; connects to Anthropic and OpenAI through one interface | Model agnostic but less agentic | Limited, requires custom API work |
| Output types | Inspect compatible transcripts, rollouts, quantitative metrics | Structured logs and benchmark scores | Human labels and raw transcripts |
| Sweeps and tooling | Integrates with Weights and Biases for large sweeps | Some support via custom tooling | Hard to scale without tooling |
| Quantitative metrics | Elicitation rate, reproducible stats, Spearman correlations | Curated metrics and aggregate scores | Limited quantitative repeatability |
| Best for | Scaling behavior driven evaluations and safety research | Targeted benchmark comparisons | Small studies and qualitative checks |
Bloom evaluation stages: Understanding, Ideation, Rollout, Judgment and meta-judgment
Bloom runs a four stage evaluation pipeline to convert seeds into scored rollouts. In practice, the framework uses agentic subroutines at each stage. Claude Opus 4.1 serves as the primary automated judge across stages for consistent scoring. For reference, see the Claude page.
Understanding
- Purpose: Parse the seed, extract intent, constraints, and success criteria.
- Example: Identify whether a seed targets misinformation, jailbreak attempts, or social engineering.
- Technical note: Agents produce structured interpretation objects that guide later steps.
Ideation
- Purpose: Generate diverse scenario variants that probe edge cases and failure modes.
- Example: Create user prompts that escalate ambiguity or request sensitive steps.
- Technical note: Ideation agents apply controlled perturbations to produce behavior consistent rollouts.
Rollout
- Purpose: Execute interactions between scenario actors and target models.
- Example: Run 100 distinct dialogues to measure how often a model elicits the target behavior.
- Technical note: Bloom records Inspect compatible transcripts and time stamped events.
Judgment and meta-judgment
- Purpose: Score transcripts, adjudicate borderline cases, and estimate judge reliability.
- Example: Claude Opus 4.1 rates each transcript, while meta-judgment aggregates confidence and disagreement.
- Technical note: Outputs include elicitation rate, reproducible statistics, and Spearman correlations used in validation.
Together, these stages let teams scale reproducible evaluations and quantify risk across frontier models.
Bloom Open-Source Agentic Framework
Bloom open-source agentic framework for automated behavioral evaluations of frontier AI models offers a scalable, reproducible path to safer systems. It automates seed-driven generation, ideation, rollout, and judgment with quantitative outputs like elicitation rate. As a result, researchers gain measurable metrics and Inspect-compatible transcripts for rigorous analysis.
Because Bloom turns one behavior definition into full evaluation suites, teams test edge cases faster. Moreover, the MIT-licensed Python pipeline integrates with LiteLLM, Anthropic, OpenAI, and Weights and Biases. Claude Opus 4.1 serves as a reliable judge, yielding high correlation with human labels. Therefore Bloom accelerates alignment research while keeping evaluations transparent and extensible.
Because Bloom is open-source, teams can fork, extend judge models, and reproduce results. Community contributions accelerate coverage across behaviors and model organisms. Moreover, Bloom complements tools like Petri for benchmark-driven comparisons.
EMP0 leads in AI and automation solutions, deploying AI-powered growth systems under client infrastructure. Visit our website at EMP0 Website and our blog at EMP0 Blog for tools and guides. Follow us on Twitter at EMP0 Twitter and read deeper posts on Medium at Medium Posts. Explore automation workflows on n8n at n8n Workflows and contact our team to accelerate safe AI adoption.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is Bloom open-source agentic framework for automated behavioral evaluations of frontier AI models?
Bloom is an open-source, agentic evaluation pipeline. It automates behavioral evaluations for frontier AI models. The framework converts a single behavior definition into many rollouts. Therefore teams get reproducible transcripts, elicitation rates, and quantitative metrics. Bloom runs as a Python pipeline under an MIT license. Because it is agentic, it ideates, rolls out, and judges scenarios automatically.
How does Bloom work in practice?
Bloom runs four stages: Understanding, Ideation, Rollout, and Judgment with meta-judgment. First, agents parse the seed and extract constraints. Next, ideation agents create diverse scenario variants. Then the pipeline executes rollouts against target models. Finally, automated judges score transcripts and estimate reliability. Bloom uses LiteLLM for model calls and can interface with Anthropic and other backends. For more on Anthropic and Claude, see Anthropic and Claude.
Why are seed.yaml and behaviors.json important?
The seed configuration defines target behavior, roles, and run parameters. seed.yaml seeds initial scenarios and constraints. behaviors.json lists behavior categories and judgment rules. Because Bloom expands a seed into many behavior consistent rollouts, seeds make evaluations reproducible and targeted. Therefore teams can tune elicitation rate and probe edge cases systematically.
How does Bloom compare with Petri?
Bloom emphasizes agentic generation and automated judgment. In contrast, Petri focuses on benchmark style, curated tests. Bloom scales behavioral coverage with automated ideation and integrates tooling like Weights and Biases at Weights and Biases. Therefore Bloom suits safety research that needs large sweeps and quantitative elicitation metrics.
Where can I find resources and get started?
Check the project repository, technical report, and documentation. Also explore Anthropic’s developer pages and tooling links above for judge model context. Finally, run sample seeds locally with the MIT-licensed Python pipeline to reproduce experiments and measure elicitation rates.

