In recent years, artificial intelligence has emerged as a transformative force in education, reshaping traditional paradigms and introducing innovative tools that promise enhanced learning experiences. Among these developments, the recent unveiling of ChatGPT’s Study Mode stands out as a beacon of excitement, offering features designed to guide learners and stimulate critical thinking. This advancement is met with enthusiasm, reflecting a growing belief that AI can play a vital role in supporting educational objectives. However, alongside this optimism are significant challenges that persist within the educational landscape—issues of equity, accessibility, and the very essence of learning itself remain at the forefront of discussions about education disruption. As we embrace these new technologies, it is crucial to remain cautious and analytical, recognizing that tools like ChatGPT’s Study Mode, while promising, do not inherently resolve the deeper problems that traditional educational systems face.
When I think back to my own educational struggles, I remember a particularly challenging math test that made my heart race and palms sweat. I felt lost, overwhelmed by the equations and concepts that seemed to mock me from the page. In that moment of vulnerability, a teacher’s encouragement and a supportive study group transformed my anxiety into confidence. Education has always been about more than just passing tests; it embodies moments of connection, growth, and resilience. This experience resonates with many learners today, highlighting how reliance on AI must not overshadow those essential human interactions and emotional support that foster true understanding. The balance between leveraging AI capabilities and addressing enduring educational challenges is where the future of learning may ultimately lie.
Potential Benefits of ChatGPT’s Study Mode
The introduction of ChatGPT’s Study Mode presents numerous potential benefits that can enhance learning experiences. Insights from Leah Belsky, a vice president of education at OpenAI, highlight how this feature aims to guide students more effectively, potentially improving their academic performance. Here are some key benefits of the Study Mode:
-
Promotes Active Engagement
By asking open-ended questions, Study Mode encourages students to think critically and engage actively with the material. This interactive approach can enhance comprehension and retention of complex topics. -
Provides Personalized Tutoring
The feature acts like a personalized tutor, helping learners at their own pace. As noted by Leah Belsky, utilizing ChatGPT in a teaching capacity can lead to significant improvements in academic performance, tailored to each student’s needs. -
Enhances Problem-Solving Skills
Through Socratic questioning, ChatGPT’s Study Mode can help students develop problem-solving skills. This method pushes learners to explore various solutions instead of simply providing answers, fostering deeper understanding. -
Accessibility for Various Learning Styles
ChatGPT’s flexibility in accommodating different learning styles allows it to provide targeted assistance that suits visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners. This inclusivity might lead to better educational outcomes across diverse student populations. -
Encourages Self-Directed Learning
By guiding students through inquiry rather than giving them straightforward answers, Study Mode promotes self-directed learning. This empowers learners to take ownership of their education, increasing motivation and interest in their studies. -
Feedback and Assessment
The capability to provide instant feedback can help students identify areas for improvement and solidify their knowledge. Immediate responses from ChatGPT can enhance the learning process by allowing students to correct misunderstandings promptly.
In conclusion, while ChatGPT’s Study Mode offers promising enhancements to tutoring and academic performance, it should be incorporated thoughtfully alongside traditional educational methods to create a balanced learning ecosystem. This reinforces the importance of human interaction and mentorship that is essential to effective education.

Challenges Posed by Generative AI in Education
As the educational landscape increasingly incorporates generative AI technologies, various challenges emerge that may undermine the potential benefits these tools might offer. Particularly, tools like ChatGPT’s Study Mode, while promising in enhancing educational processes, do not necessarily tackle more profound issues within learning environments.
Transitioning from the potential advantages of AI tools, it is essential to delve into the challenges that arise. Understanding these hurdles allows us to appreciate the context in which AI adoption occurs.
- Learning Outcomes and Critical Thinking
One pressing concern about generative AI in education is its impact on learning outcomes. Students may become overly dependent on AI tools for information retrieval, which risks stifling their development of critical thinking and analytical skills. Instead of engaging deeply with content, learners might resort to accepting AI-generated information passively, thus diminishing their capacity for independent thought and creative problem-solving. As noted in a study on generative AI, students who heavily rely on these tools often show reduced engagement and lack an essential foundation of deep learning experiences [ProQuest]. - Equity and Accessibility
Generative AI’s integration into education highlights the risk of widening the digital divide. Not all students have equal access to technology and the internet, particularly in under-resourced communities. As highlighted in a recent report, students from disadvantaged backgrounds tend to be left out of the conversations surrounding AI-enhanced education due to a lack of proper infrastructure and resources. This inequity can exacerbate existing educational disparities rather than alleviate them [Springer]. - Student Engagement and Human Interaction
An increased reliance on AI tools may undercut the essential human interactions that contribute to a robust educational experience. The emotional and social aspects of learning—interactions between students and educators—are vital for social skill development and fostering emotional intelligence. Without these engagements, students might find themselves lacking in essential soft skills necessary for real-world success [Academik America]. - Autonomy and the Role of Educators
The growing role of AI in classroom settings raises concerns about educators’ influence and autonomy in the teaching process. As automated systems become more prevalent, there is a risk that teachers could become sidelined, thereby diminishing the quality of instruction. Furthermore, students may turn into passive recipients of information rather than active participants in their education, undermining the development of self-directed learning skills [Springer]. - Bias and Fairness
Finally, generative AI is often influenced by the datasets used for training, which can contain inherent biases. This raises significant concerns regarding fairness and inclusivity in educational content. Bias can have detrimental effects on student outcomes, particularly for marginalized groups. Ensuring that AI-generated educational materials do not perpetuate stereotypes or discrimination is vital for fostering an equitable learning environment [PMC].
In conclusion, while generative AI such as ChatGPT presents innovative potential to enhance education, it is critical to address these challenges thoughtfully. By focusing on equitable access, valuing human interaction, promoting critical engagement, and ensuring ethical AI deployment, we can utilize these technologies to foster a more effective educational landscape that benefits all learners.
User Adoption of AI Tools in K-12 Education
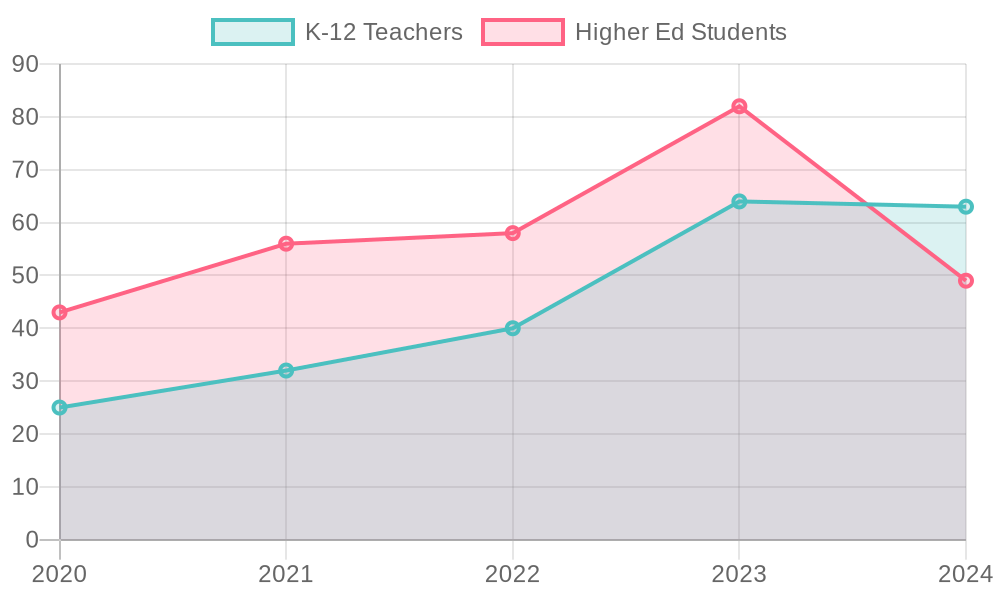
Recent statistics indicate a significant rise in the adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) tools within K-12 education, reflecting the growing integration of these technologies in educational practices. A report by the Center for Democracy & Technology revealed that the percentage of K-12 teachers utilizing generative AI tools for personal or professional purposes increased by 32 percentage points, reaching 83% between the 2022-2023 and 2023-2024 school years (NEA).
Student usage is also noteworthy; a survey conducted in early 2023 found that 89% of students reported using ChatGPT for completing homework assignments (Engageli). This rapid uptake signifies an integration of AI tools into daily learning processes, facilitating access to information and support for students seeking assistance outside of traditional classroom settings.
In terms of professional development, a study by the RAND Corporation highlighted that by fall 2024, 48% of school districts had implemented training programs for teachers on using AI, up from 23% in the previous year. However, disparities in training access were observed based on district wealth; in fall 2023, only 6% of high-poverty districts provided AI training for teachers, compared to 43% in low-poverty districts (RAND).
One compelling case study comes from the Newark school district, which launched a pilot of “Khanmigo,” an AI tutor developed by Khan Academy, during the 2023-2024 school year. This AI tool was used by students in grades 5–8 at First Avenue School to support their learning in subjects such as math, reading, and writing. The successful pilot resulted in expansion to 13 additional schools, with early indicators showing improvements in math proficiency and overall student engagement (LinkedIn).
These statistics and case studies highlight the transformative potential of AI integration in K-12 education. However, they also suggest the need for ongoing vigilance to ensure equitable access to these resources and training, particularly in underserved communities.
| AI Tool | Tutoring Capabilities | User Interface | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|
| ChatGPT | Personalized tutoring via Study Mode | Intuitive and user-friendly | Proven to improve academic performance significantly when used as a tutor. |
| Gauth | Customizable tutoring experiences | Simple and accessible | Demonstrated flexibility in catering to diverse learning needs. |
| IBM Watson | Collaborative learning support | Professional UI | Effectiveness in enhancing engagement through interactive tasks. |
| Google AI Tutor | Basic tutoring suggestions | User-friendly | Effectiveness varies based on user engagement; basic support provided. |
| Squirrel AI | Adaptive learning paths | Engaging interface | High effectiveness in personalized learning environments with AI-driven assessments. |
Conclusion
The emergence of AI tools like ChatGPT’s Study Mode presents both exciting opportunities and formidable challenges in the educational landscape. While the potential for these technologies to enhance learning experiences is significant, it is essential to approach their integration with caution. As highlighted throughout this article, the reliance on AI may risk stifling critical thinking and analytical skills in students if not utilized effectively. Encouraging vibrant, independent thought must remain a priority in any educational framework.
Moreover, the ethical implications of AI in education necessitate ongoing discourse. Issues such as accessibility, equity, and the role of human interaction must not be overshadowed by the allure of technological advancements. To foster meaningful learning outcomes, educators and policymakers alike must ensure that AI tools complement traditional teaching methods rather than replace them.
Moving forward, it is crucial to address these challenges proactively and engage in critical thinking about the future of learning. By doing so, we can create an educational environment that leverages AI tools responsibly, promoting equitable access and enhancing the overall quality of education for all students.
Conclusion
The emergence of AI tools like ChatGPT’s Study Mode presents both exciting opportunities and formidable challenges in the educational landscape. While the potential for these technologies to enhance learning experiences is significant, it is essential to approach their integration with caution. As highlighted throughout this article, the reliance on AI may risk stifling critical thinking and analytical skills in students if not utilized effectively. Encouraging vibrant, independent thought must remain a priority in any educational framework.
Moreover, the ethical implications of AI in education necessitate ongoing discourse. Issues such as accessibility, equity, and the role of human interaction must not be overshadowed by the allure of technological advancements. Leah Belsky has emphasized that generative AI, when utilized in a responsible manner, could create a democratizing force in education and should complement the teaching done by educators: “We can build a brighter future… finding the appropriate way to teach schoolchildren how to use it responsibly and well.”
To foster meaningful learning outcomes, educators and policymakers alike must ensure that AI tools complement traditional teaching methods rather than replace them.
Moving forward, it is crucial to address these challenges proactively and engage in critical thinking about the future of learning. By doing so, we can create an educational environment that leverages AI tools responsibly, promoting equitable access and enhancing the overall quality of education for all students.
Insight Quotes from Educational Leaders
In the context of integrating AI into education, several key insights from educational leaders provide depth to the ongoing discussion. Leah Belsky, Vice President and General Manager of Education at OpenAI, has expressed significant points about the role and responsibility of AI in educational environments:
-
On the democratizing potential of AI in education: Belsky pointed out that AI can offer personalized tutoring opportunities for students lacking resources, stating, “Generative AI has the potential to be an extremely democratizing force… to give everyone the… personalized AI tutor that helps them learn faster.”
Source: Washington Post -
On the importance of responsible AI integration: She emphasized the significance of careful implementation by noting that, “So long as we do it responsibly, we can build a brighter future… finding the appropriate way to teach schoolchildren how to use it responsibly and well.”
Source: Washington Post -
On AI’s transformative role in education: Belsky expressed her hopes for AI in solving longstanding issues, stating, “I hope to help realize the potential of AI to solve deep challenges in education and ensure that everyone… can access AI and unlock its benefits.”
Source: LinkedIn
While insights from Abhi Muchhal were not publicly available, his past discussions have reinforced the idea that educators should prioritize the context in which AI tools are utilized and the questions they help students explore, emphasizing the importance of generating self-directed inquiry during learning processes.
These insights underscore not only the potential of AI like ChatGPT to enhance educational experiences but also the necessity for a thoughtful approach to its integration into learning frameworks to foster critical thinking and equitable access.
Future Implications of AI in Education
As artificial intelligence continues to evolve, its implications for education remain profound and multi-faceted. The advancement of tools like ChatGPT is expected to significantly shape the educational landscape, creating new opportunities and challenges as we transition into this new era of learning.
Transformative Learning Experiences
The use of AI will likely foster personalized learning experiences unlike any seen before. AI tools can adapt to individual learning styles, pacing, and preferences, potentially enhancing student engagement and achievement. With the ability to analyze vast amounts of data, AI can identify learning gaps and tailor resources specifically to address these needs, thus promoting a more effective educational journey.
Integration of AI as an Educational Partner
As AI becomes more sophisticated, it is poised to act as a collaborative partner in education. Rather than serving merely as a tool for information retrieval, AI could help foster discussions, mentor students, and stimulate critical thinking. This shift could redefine the role of educators, who might transition into facilitators of learning experiences rather than mere dispensers of knowledge. Such integration could lead to enriched classroom dynamics, where human interaction complements AI capabilities, cultivating a more holistic educational environment.
Ethical Considerations and The Need for Guidelines
However, the rise of AI in education necessitates a cautious approach. Ethical considerations surrounding data privacy, equity, and the potential for bias in AI algorithms must be part of any conversation about its use. Educators and policymakers will need to establish guidelines to ensure that these tools are used responsibly, maximizing potential benefits while mitigating risks. The reliance on AI can inadvertently lead to diminished critical thinking skills if students become overly reliant on technology for problem-solving and inquiry.
Equity and Accessibility
Moreover, as AI tools become mainstream, the digital divide remains a pressing concern. Access to reliable technology and the internet is not uniform; thus, there is a risk that AI could exacerbate existing disparities in educational outcomes. Ensuring that all students, regardless of background, have equal access to AI resources will be critical in preventing further inequities within education.
In conclusion, the future of AI in education is filled with potential for innovation and disruption. As we harness these powerful tools, maintaining a keen awareness of the ethical implications and ensuring equitable access will be paramount in shaping a beneficial educational landscape for all learners.
In recent years, artificial intelligence has emerged as a transformative force in education, reshaping traditional paradigms and introducing innovative tools that promise enhanced learning experiences in classrooms. Among these developments, the recent unveiling of ChatGPT’s Study Mode stands out as a beacon of excitement, offering features designed to guide learners and stimulate critical thinking. This advancement is met with enthusiasm, reflecting a growing belief that AI can play a vital role in supporting educational objectives within the realm of educational technology. However, alongside this optimism are significant challenges that persist within the educational landscape—issues of equity, accessibility, and the very essence of learning itself remain at the forefront of discussions about AI integration in classrooms and education disruption. As we embrace these new technologies, it is crucial to remain cautious and analytical, recognizing that tools like ChatGPT’s Study Mode, while promising, do not inherently resolve the deeper problems that traditional educational systems face.
When I think back to my own educational struggles, I remember a particularly challenging math test that made my heart race and palms sweat. I felt lost, overwhelmed by the equations and concepts that seemed to mock me from the page. In that moment of vulnerability, a teacher’s encouragement and a supportive study group transformed my anxiety into confidence. This experience resonates with many learners today, highlighting how reliance on AI tools for education must not overshadow those essential human interactions and emotional support that foster true understanding. The balance between leveraging AI capabilities and addressing enduring educational challenges is where the future of educational technology may ultimately lie.

